PCI Compliance Explainers:
PCI Compliance: The 12 Requirements and Compliance Checklist
The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI-DSS) is a binding set of requirements for any organization that processes or stores credit card information. We’ll briefly review PCI compliance and its main requirements, and provide a list of easy best practices you can implement in your organization to comply with the PCI standards.
This is part of an extensive series of guides about compliance management.
What Is PCI Compliance?
The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standards (PCI DSS) applies to any company storing processing, or transmitting credit card data. It facilitates the comprehensive adoption of consistent data security measures. Web companies must follow the requirements of the PCI DSS, including a variety of measures, such as hosting the data with a PCI-compliant host. PCI DSS is an organization formed by the major credit card companies, such as Visa, Mastercard, Discover, and American Express.
The main goal of PCI compliance is to reduce the opportunities for attack. This involves using a secure Card Data Environment (CDE), and this applies regardless of whether you use your in-house environment or a third-party secure payment option. This is especially important for e-commerce sites, which rely exclusively on the transfer of payment card data through the internet.
Some risks involving e-commerce websites are, for example:
- Credit card fraud – attackers make purchases using stolen credit cards or credit card numbers.
- Identity theft – attackers pretend to be someone else and make purchases using their credentials.
- Credit card hijacking – attacks redirect customers to a fake shopping cart, hijack their session, or use other means to compromise credit card data.
Any e-commerce organization’s security strategy requires a continuous effort to ensure compliance. Compliance with PCI affects not only merchants but also universities, banks, municipalities, or in fact any organization from the public or private sector that handles credit card data. Since early 2019, this includes software developers that design software or web applications that accept credit card payments.
What Happens If You’re Not PCI Compliant?
If a company is found non-compliant with PCI-DSS, the penalties and consequences range from fines to the loss of permission to accept credit card payments.
Some of the penalties include:
- Inability to accept payments by credit card – the most severe penalty for many businesses is the inability to accept payments by credit card at all. This can create massive financial losses, loss of market share, and damage to reputation. An organization suffering this penalty needs to undergo a PCI reassessment by an external Quality Security Assessor (QSA) to regain permission to process payments.
- Fines – the penalty for a non-PCI compliant website typically ranges from $86,000 to $4 million.
- Mandatory forensic examination – when a data breach is suspected, merchants are required to undergo a mandatory forensic examination, which can cost between $20,000 and $50,000 for a Level 2 merchant (1-6 million annual transactions), and upward of $120,000 for a Level 1 merchant (6+ million annual transactions).
- Liability for fraud charges – following a security breach, a company is exposed to lawsuits, as it is the merchant’s responsibility to keep its customer’s sensitive information safe.
The 12 Requirements for PCI DSS Compliance
The PCI DSS is composed of six goals and twelve requirements, as follows:
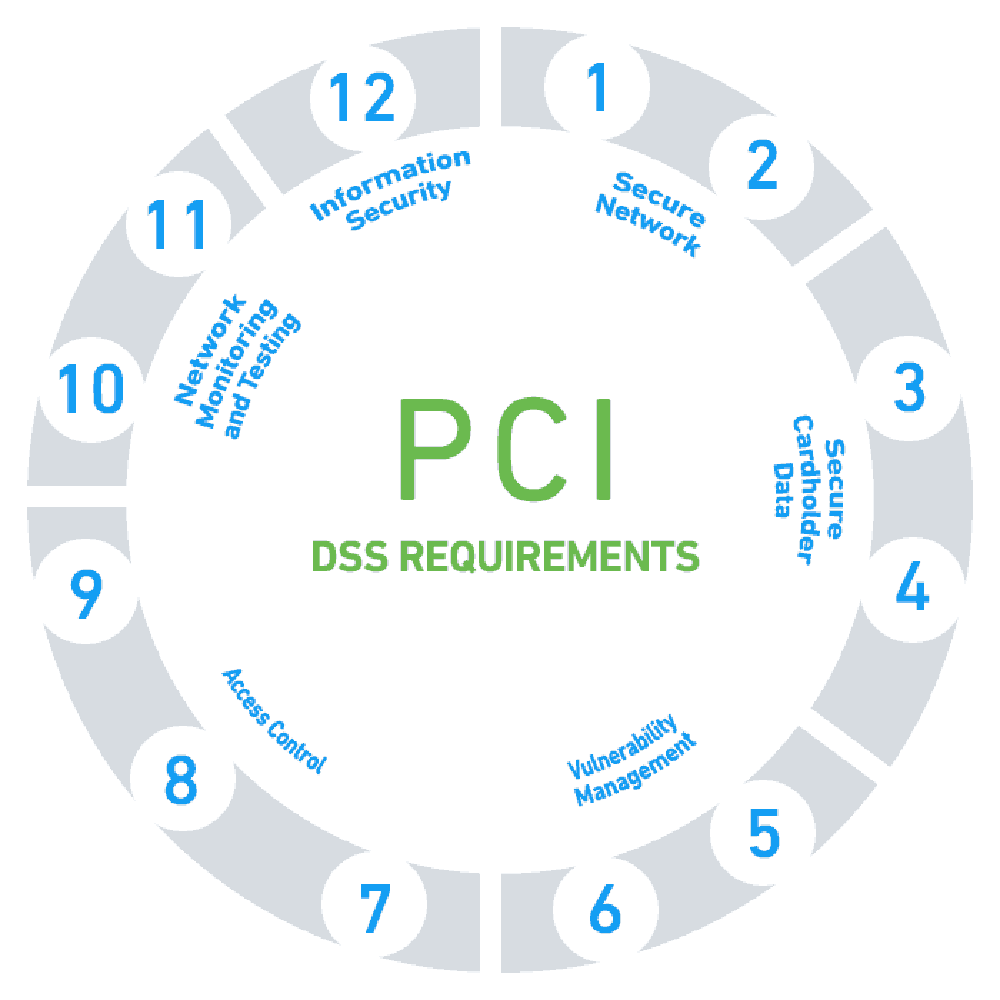
The PCI DSS outlines 12 key requirements for businesses to be compliant. These are divided into six different categories, each focusing on a specific aspect of information security. Let’s break them down:
1. Use and Maintain Firewalls
Firewalls are a crucial line of defense in securing your network. They monitor and control incoming and outgoing network traffic based on security rules and establish a barrier between your secure internal network and potentially insecure external networks. Therefore, it’s essential to use and maintain firewalls properly to prevent unauthorized access to your network and protect cardholder data.
2. Proper Password Protections
Passwords are often the first line of defense when it comes to protecting sensitive information. Therefore, it’s important to implement strong password policies. This includes using complex passwords, regularly changing passwords, and not using vendor-supplied defaults for system passwords and other security parameters.
3. Protect Cardholder Data
Protecting cardholder data is at the heart of PCI compliance. This includes keeping stored cardholder data to a minimum, disposing of it securely when it’s no longer needed, and implementing robust access control measures to prevent unauthorized access.
4. Encryption of Transmitted Cardholder Data
Whenever cardholder data is transmitted over open networks, it becomes vulnerable to interception. Therefore, it’s important to use strong encryption methods to protect sensitive information during transmission. This ensures that even if the data is intercepted, it cannot be read without the correct decryption key.
5. Utilize Antivirus and Anti-malware Software
Antivirus and anti-malware software are essential tools for detecting and removing malicious software. They help protect your systems from threats that can compromise cardholder data and disrupt your operations. It’s important to keep these tools updated to ensure they can effectively combat the latest threats.
6. Properly Updated Software
Keeping your software updated is crucial for maintaining a secure environment. Software updates often include patches for security vulnerabilities, so outdated software can leave your systems vulnerable to attacks. Regularly updating your software helps protect against these threats and maintain the integrity of cardholder data.
7. Restrict Data Access
Access to cardholder data should be restricted on a need-to-know basis. This means that only individuals who need access to the data to perform their job should have it. Implementing strict access control measures can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access to sensitive information.
8. Unique IDs Assigned to Those with Access to Data
Each person who has access to cardholder data should be assigned a unique ID. This allows you to track and monitor individual access to data and helps in identifying any unauthorized access or suspicious activity.
9. Restrict Physical Access
Physical security is just as important as digital security when it comes to protecting cardholder data. Physical access to data and systems should be restricted and monitored to prevent unauthorized access and manipulation.
10. Create and Monitor Access Logs
Logging and monitoring access to network resources and cardholder data allows you to identify and respond to security incidents promptly. Regularly reviewing access logs can help you spot suspicious activity and prevent potential data breaches.
11. Test Security Systems on a Regular Basis
Regular testing of security systems and processes is essential to ensure they are working as intended and to identify any potential vulnerabilities. This includes testing firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and other key security measures.
12. Document Policies
Documenting your security policies and procedures is a crucial part of PCI compliance. This provides a clear framework for your team to follow and ensures that everyone understands their responsibilities when it comes to maintaining a secure environment.
PCI Compliance Checklist – Achieving PCI DSS Compliance
To comply with the PCI DSS, an organization should follow three steps:
Step 1: Assess
The assessment stage involves identifying cardholder data, taking an inventory of your IT assets and business processes for payment card processing, and analyzing them for vulnerabilities. This stage is critical because it allows you to understand where cardholder data resides within your business, how it’s processed, and where potential vulnerabilities may exist.
To begin with, you should document all the systems and processes involved in storing, processing, or transmitting cardholder data. This includes not only your payment systems but also any systems connected to them. Remember, a vulnerability in any system connected to your payment systems could potentially be exploited to gain access to cardholder data.
Next, you should conduct a vulnerability scan and penetration testing to identify potential security weaknesses. These tests should be conducted both internally and externally, and they should cover all system components defined in the PCI DSS scope.
Step 2: Remediate
The remediation phase involves fixing the vulnerabilities identified during the assessment phase. This can be a complex process, depending on the size of your business and the number of vulnerabilities identified. However, it’s a critical step in achieving PCI compliance.
Firstly, you should prioritize the vulnerabilities based on their risk level. High-risk vulnerabilities should be addressed first, as they pose the most significant threat to your cardholder data. Once these vulnerabilities have been remediated, you can then focus on lower-risk vulnerabilities.
Remediation may involve several different activities, such as patching software, updating firewalls, changing passwords, or even redesigning your business processes. It’s important to remember that remediation is not a one-time activity. New vulnerabilities can emerge at any time, so you should constantly monitor your systems and conduct regular vulnerability scans to ensure ongoing compliance.
Step 3: Report
The final phase of achieving PCI compliance is reporting. This involves compiling and submitting a report to your acquiring bank and the major payment card brands to verify compliance. The type of report required depends on the size of your business and the number of transactions you process annually.
Most small businesses are required to complete a Self-Assessment Questionnaire (SAQ), while larger businesses may need to undergo an onsite audit by a Qualified Security Assessor (QSA) or Internal Security Assessor (ISA).
Reporting is not just about proving compliance; it’s also an opportunity to reflect on your security practices and look for ways to improve. The reporting process can provide valuable insights into your security posture and help you identify areas where you can strengthen your defenses.
PCI Compliance Best Practices
The following best practices can help you improve security measures, to more easily comply with PCI-DSS security requirements.
Use a firewall – Per the first requirement, you’ll need to install a reliable firewall to protect your network and run regular testing to ensure efficiency.
Do not use default passwords – To be in PCI compliance, you must ensure all devices and user accounts use passwords that are unique, and that includes lowercase and capital letters, numbers and symbols, to make them more secure.
Use both digital and physical measures to protect cardholder data – The PCI standard requires you to put in place electronic and physical barriers to prevent unauthorized access to passwords. Some of these barriers may include authentication protocols, strong password policies, locked servers and locked cabinets for sensitive physical data. A related measure is restricting access to cardholder data and encrypting the transmission of cardholder information.
Create and enforce a security policy – A security policy should be drafted, supported by management, and made known across the organization, as well as to third-party vendors and customers. You should include a summary of how you protect customer data, explaining password and access requirements.
Establish an incident response process – Have a clear process for detecting, remediating, mitigating and recovering from security incidents.
Keep track of changes – Identify and review changes made to processes or technologies affecting cardholder data. Establish change controls, identifying the impact on compliance for every change.
Keep software patched and install security updates – Many of the world’s biggest security breaches resulted from an exploit of a known software vulnerability. Keeping software up to date, scanning systems for vulnerabilities and remediating them, is a critical defensive measure.
Conclusion
Not complying with PCI standards can result in heavy fines and other consequences, such as loss of business. A Ponemon Institute study showed that more than half of customers lost trust in an organization after it suffered a data breach, and 31 percent terminated their relationship with the organization after a breach.
Complying with PCI DSS standards is critical for the survival and success of any organization, especially those in the e-commerce industry.
See Exabeam in action: Request a demo
See Our Additional Guides on Key Compliance Management Topics
Together with our content partners, we have authored in-depth guides on several other topics that can also be useful as you explore the world of compliance management.
GDPR Compliance
Authored by Exabeam
- GDPR Compliance: A Practical Guide
- GDPR Fines Structure and the Biggest GDPR Fines to Date
- The Main GDPR Requirements in Plain English
CIAM
Authored by Frontegg
- What is Customer Identity and Access Management (CIAM)?
- Understanding the Okta CIAM Solution: Okta Identity Cloud
- CIAM vs. IAM: 5 Key Differences and How to Choose
Data Compliance
Authored by NetApp CDS